Publications
Publications in reversed chronological order.
2025
- Mulaqua
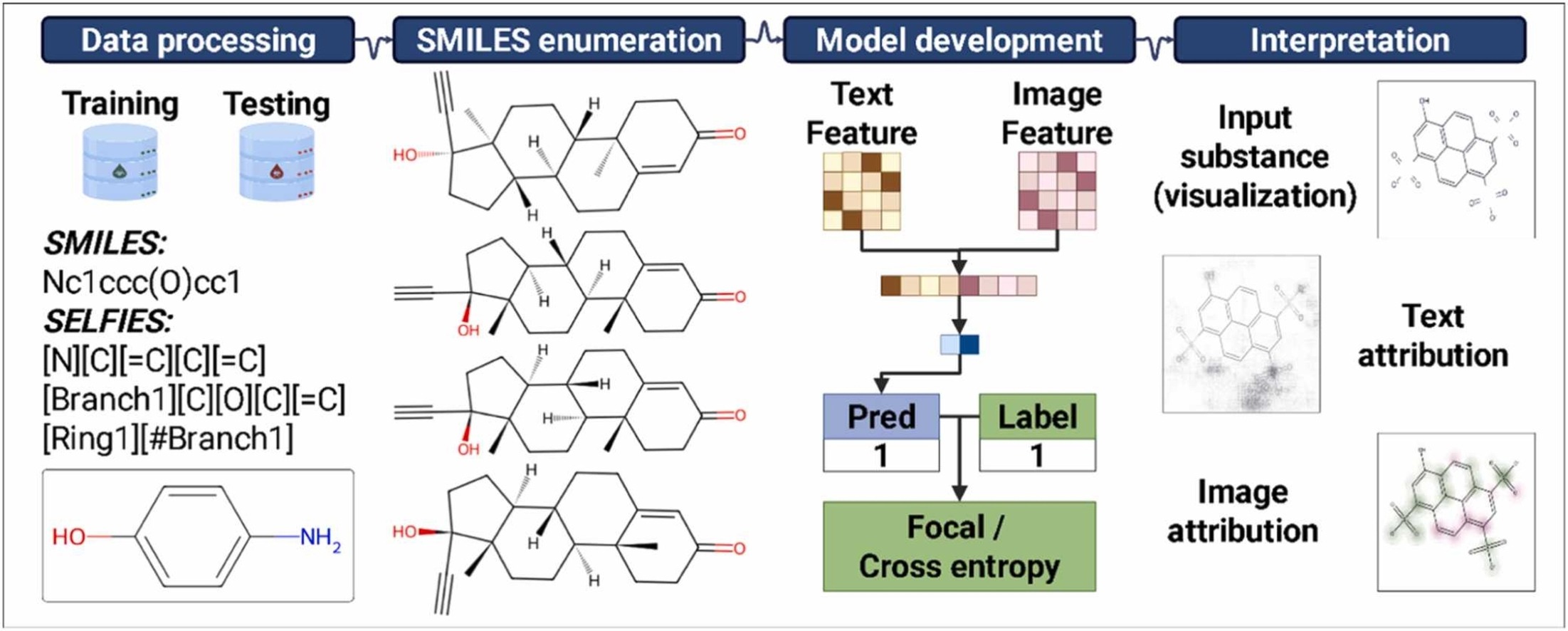 Mulaqua: An interpretable multimodal deep learning framework for identifying PMT/vPvM substances in drinking waterNguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Nhat Truong Pham, Hojin Seo, and 2 more authorsJournal of Hazardous Materials, 2025
Mulaqua: An interpretable multimodal deep learning framework for identifying PMT/vPvM substances in drinking waterNguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Nhat Truong Pham, Hojin Seo, and 2 more authorsJournal of Hazardous Materials, 2025Drinking water is an essential resource for human health and well-being, still it faces increasing threats from contamination by chemical pollutants. Among the contaminants, persistent, mobile, and toxic (PMT) substances, along with very persistent and very mobile (vPvM) substances, have emerged as chemicals of significant concern due to their harmful effects on human health. Regulatory bodies have recognized them as emerging contaminants requiring stricter monitoring and management practices. Traditional experimental methods for detecting and characterizing these substances are often slow and resource-intensive. Therefore, there is a pressing need to develop efficient computational approaches to detect persistent, mobile, and toxic, or very persistent and very mobile (PMT/vPvM) substances rapidly and economically. Addressing this gap, we proposed Mulaqua, the first deep learning (DL) approach specifically designed for identifying PMT/vPvM substances. Mulaqua utilizes a novel multimodal approach combining molecular string representation with molecular image for the final prediction. To address the data imbalance issue in the training dataset, we employ a data augmentation strategy based on Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES) enumeration, which helped to achieve a balanced performance with the training accuracy (ACC), F1-score (F1), and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) score of 0.920, 0.590, and 0.548, respectively. Our study also includes interpretability analyses to elucidate how specific molecular architectures influence PMT/vPvM substances characterization, thereby providing meaningful insights. Mulaqua demonstrates excellent transferability, validated through rigorous evaluation of external datasets, which significantly improves performance compared to the baseline. Unlike previous methods, Mulaqua is now publicly available at https://github.com/cbbl-skku-org/Mulaqua/, holds significant potential as a proactive tool for early hazard identification and regulatory prioritization of PMT/vPvM substances in environmental risk management.
@article{NGUYEN2025140573, bibtex_show = true, dimensions = {true}, title = {Mulaqua: An interpretable multimodal deep learning framework for identifying PMT/vPvM substances in drinking water}, journal = {Journal of Hazardous Materials}, volume = {500}, pages = {140573}, year = {2025}, issn = {0304-3894}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.140573}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389425034934}, author = {Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Pham, Nhat Truong and Seo, Hojin and Wei, Leyi and Manavalan, Balachandran}, keywords = {PMT/vPvM substances, Water quality, Data augmentation, Multimodal deep learning, Model interpretation} } - xBitterT5
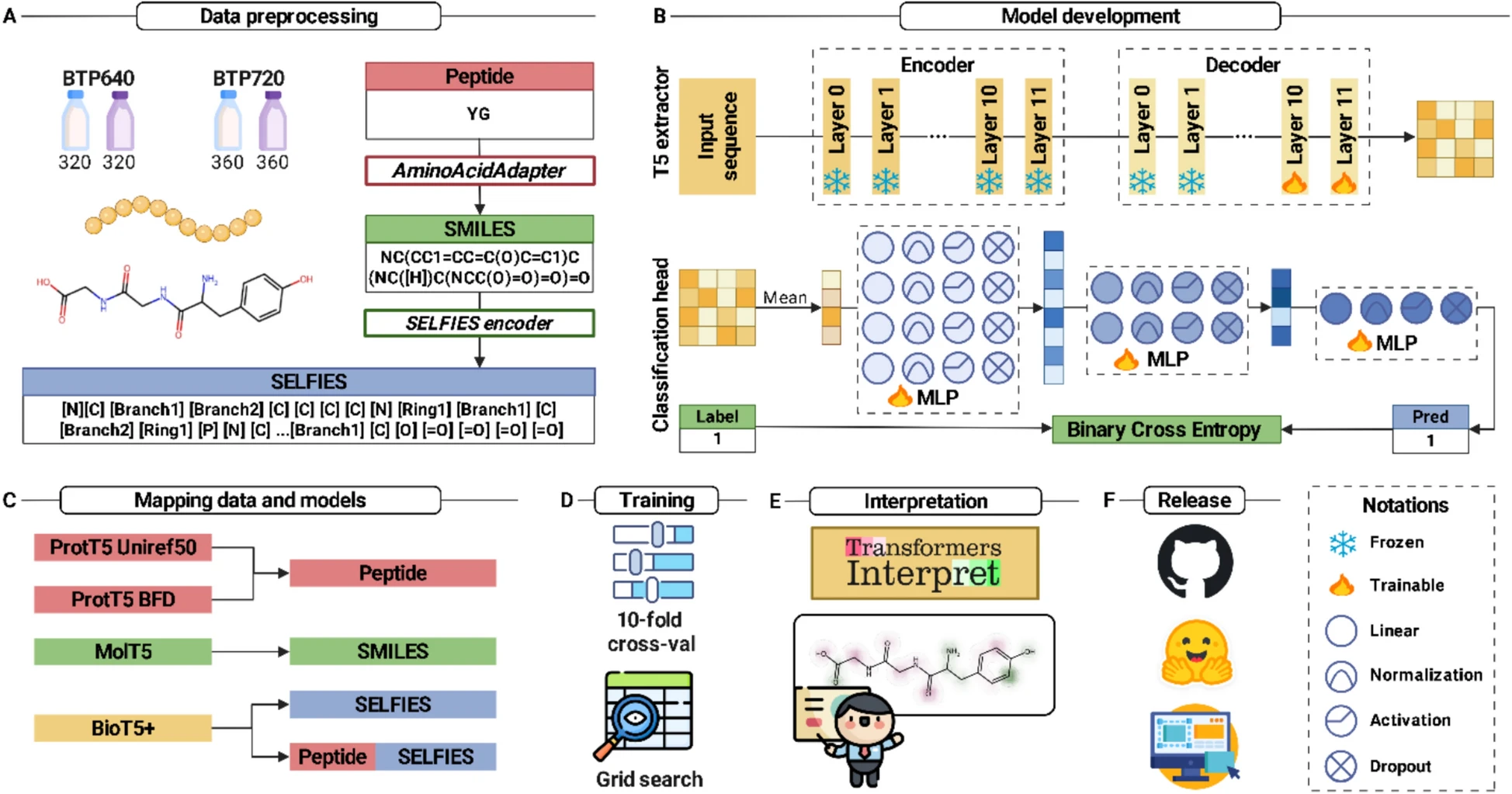 xBitterT5: an explainable transformer-based framework with multimodal inputs for identifying bitter-taste peptidesNguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Nhat Truong Pham, Duong Thanh Tran, and 3 more authorsJournal of Cheminformatics, Aug 2025
xBitterT5: an explainable transformer-based framework with multimodal inputs for identifying bitter-taste peptidesNguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Nhat Truong Pham, Duong Thanh Tran, and 3 more authorsJournal of Cheminformatics, Aug 2025Bitter peptides (BPs), derived from the hydrolysis of proteins in food, play a crucial role in both food science and biomedicine by influencing taste perception and participating in various physiological processes. Accurate identification of BPs is essential for understanding food quality and potential health impacts. Traditional machine learning approaches for BP identification have relied on conventional feature descriptors, achieving moderate success but struggling with the complexities of biological sequence data. Recent advances utilizing protein language model embedding and meta-learning approaches have improved the accuracy, but frequently neglect the molecular representations of peptides and lack interpretability. In this study, we propose xBitterT5, a novel multimodal and interpretable framework for BP identification that integrates pretrained transformer-based embeddings from BioT5+\thinspacewith the combination of peptide sequence and its SELFIES molecular representation. Specifically, incorporating both peptide sequences and their molecular strings, xBitterT5 demonstrates superior performance compared to previous methods on the same benchmark datasets. Importantly, the model provides residue-level interpretability, highlighting chemically meaningful substructures that significantly contribute to its bitterness, thus offering mechanistic insights beyond black-box predictions. A user-friendly web server (https://balalab-skku.org/xBitterT5/) and a standalone version (https://github.com/cbbl-skku-org/xBitterT5/) are freely available to support both computational biologists and experimental researchers in peptide-based food and biomedicine.
@article{Nguyen2025, bibtex_show = true, dimensions = {true}, author = {Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Pham, Nhat Truong and Tran, Duong Thanh and Wei, Leyi and Malik, Adeel and Manavalan, Balachandran}, title = {xBitterT5: an explainable transformer-based framework with multimodal inputs for identifying bitter-taste peptides}, journal = {Journal of Cheminformatics}, year = {2025}, month = aug, day = {20}, volume = {17}, number = {1}, pages = {127}, issn = {1758-2946}, doi = {10.1186/s13321-025-01078-1}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-025-01078-1} } - HyPepTox-Fuse
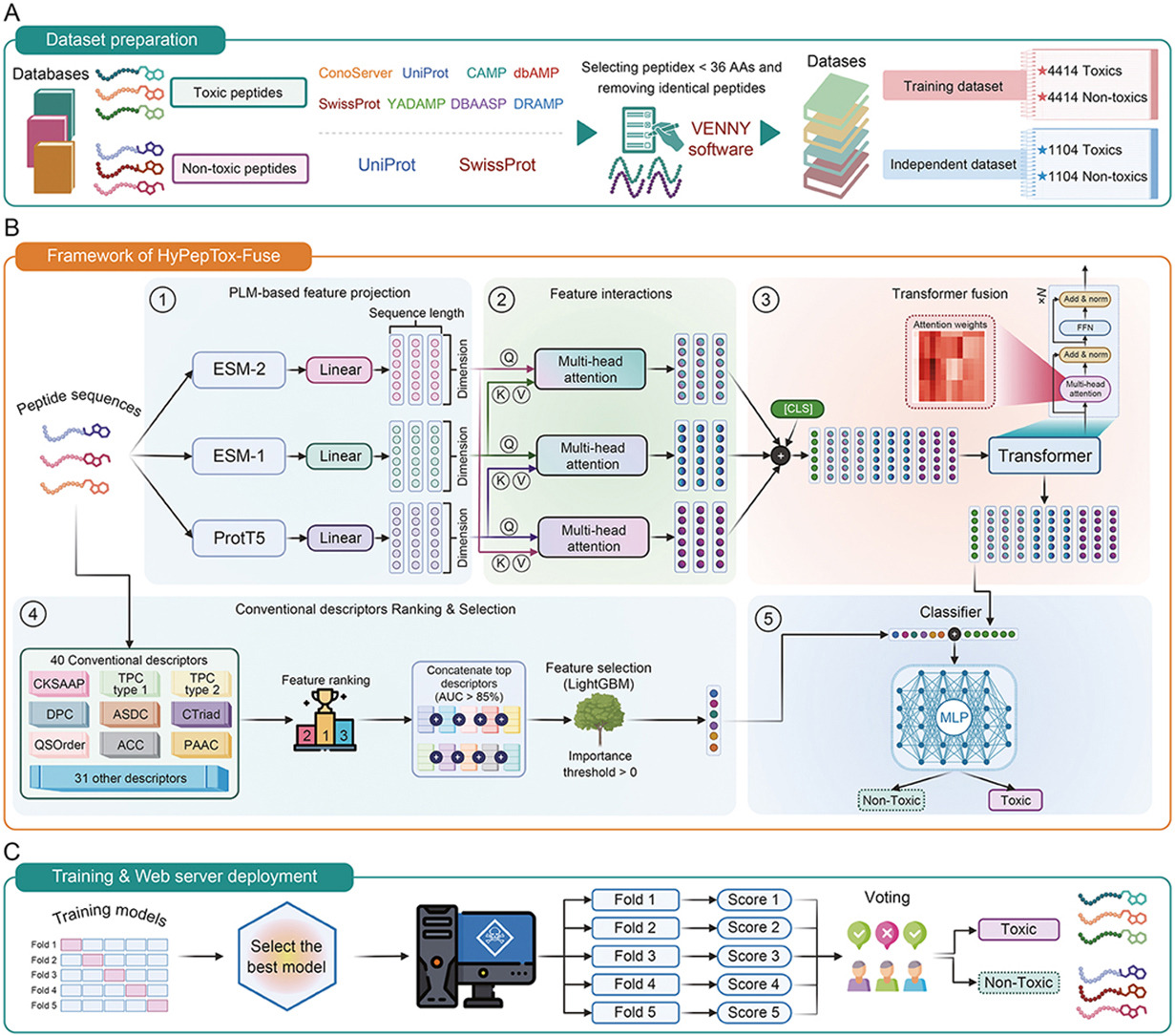 HyPepTox-Fuse: An interpretable hybrid framework for accurate peptide toxicity prediction fusing protein language model-based embeddings with conventional descriptorsDuong Thanh Tran, Nhat Truong Pham, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, and 2 more authorsJournal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Aug 2025
HyPepTox-Fuse: An interpretable hybrid framework for accurate peptide toxicity prediction fusing protein language model-based embeddings with conventional descriptorsDuong Thanh Tran, Nhat Truong Pham, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, and 2 more authorsJournal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Aug 2025Peptide-based therapeutics hold great promise for the treatment of various diseases; however, their clinical application is often hindered by toxicity challenges. The accurate prediction of peptide toxicity is crucial for designing safe peptide-based therapeutics. While traditional experimental approaches are time-consuming and expensive, computational methods have emerged as viable alternatives, including similarity-based and machine learning (ML)-/deep learning (DL)-based methods. However, existing methods often struggle with robustness and generalizability. To address these challenges, we propose HyPepTox-Fuse, a novel framework that fuses protein language model (PLM)-based embeddings with conventional descriptors. HyPepTox-Fuse integrates ensemble PLM-based embeddings to achieve richer peptide representations by leveraging a cross-modal multi-head attention mechanism and Transformer architecture. A robust feature ranking and selection pipeline further refines conventional descriptors, thus enhancing prediction performance. Our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cross-validation and independent evaluations, offering a scalable and reliable tool for peptide toxicity prediction. Moreover, we conducted a case study to validate the robustness and generalizability of HyPepTox-Fuse, highlighting its effectiveness in enhancing model performance. Furthermore, the HyPepTox-Fuse server is freely accessible at https://balalab-skku.org/HyPepTox-Fuse/ and the source code is publicly available at https://github.com/cbbl-skku-org/HyPepTox-Fuse/. The study thus presents an intuitive platform for predicting peptide toxicity and supports reproducibility through openly available datasets.
@article{TRAN2025101410, bibtex_show = true, dimensions = {true}, title = {HyPepTox-Fuse: An interpretable hybrid framework for accurate peptide toxicity prediction fusing protein language model-based embeddings with conventional descriptors}, journal = {Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis}, volume = {15}, number = {8}, pages = {101410}, year = {2025}, issn = {2095-1779}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2025.101410}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095177925002278}, author = {Tran, Duong Thanh and Pham, Nhat Truong and Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Wei, Leyi and Manavalan, Balachandran}, keywords = {Peptide toxicity, Hybrid framework, Multi-head attention, Transformer, Deep learning, Machine learning, Protein language model} } - XMolCap
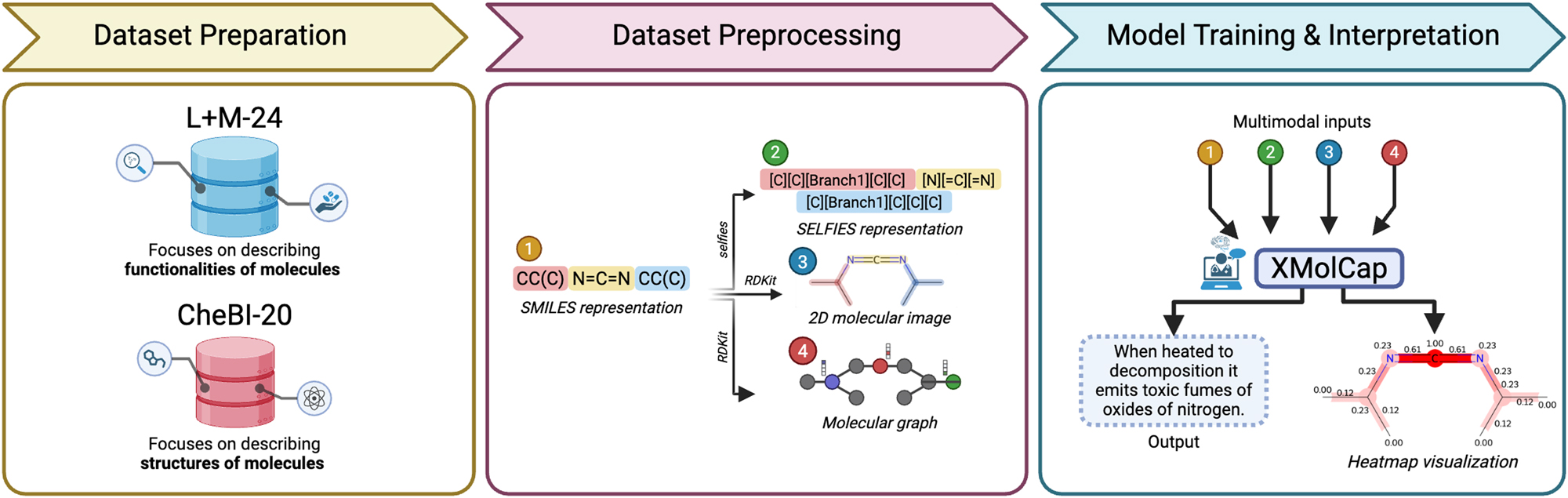 XMolCap: Advancing Molecular Captioning Through Multimodal Fusion and Explainable Graph Neural NetworksDuong Thanh Tran, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Nhat Truong Pham, and 3 more authorsIEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, Oct 2025
XMolCap: Advancing Molecular Captioning Through Multimodal Fusion and Explainable Graph Neural NetworksDuong Thanh Tran, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Nhat Truong Pham, and 3 more authorsIEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, Oct 2025Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced computational biology by enabling the integration of molecular, protein, and natural language data to accelerate drug discovery. However, existing molecular captioning approaches often underutilize diverse molecular modalities and lack interpretability. In this study, we introduce XMolCap, a novel explainable molecular captioning framework that integrates molecular images, SMILES strings, and graph-based structures through a stacked multimodal fusion mechanism. The framework is built upon a BioT5-based encoder-decoder architecture, which serves as the backbone for extracting feature representations from SELFIES. By leveraging specialized models such as SwinOCSR, SciBERT, and GIN-MoMu, XMolCap effectively captures complementary information from each modality. Our model not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmark datasets (L+M-24 and ChEBI-20), outperforming several strong baselines, but also provides detailed, functional group-aware, and property-specific explanations through graph-based interpretation. XMolCap is publicly available at https://github.com/cbbl-skku-org/XMolCap/ for reproducibility and local deployment. We believe it holds strong potential for clinical and pharmaceutical applications by generating accurate, interpretable molecular descriptions that deepen our understanding of molecular properties and interactions.
@article{11012653, bibtex_show = true, dimensions = {true}, author = {Tran, Duong Thanh and Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Pham, Nhat Truong and Rakkiyappan, Rajan and Karki, Rajendra and Manavalan, Balachandran}, journal = {IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics}, title = {XMolCap: Advancing Molecular Captioning Through Multimodal Fusion and Explainable Graph Neural Networks}, year = {2025}, volume = {29}, number = {10}, pages = {7034-7045}, keywords = {Biological system modeling;Feature extraction;Chemicals;Bioinformatics;Accuracy;Training;Data models;Data mining;Transformers;Encoding;Explainable artificial intelligence;graph neural networks;language and molecules;large language models;molecular captioning;model interpretation;multimodal fusion}, doi = {10.1109/JBHI.2025.3572910}, issn = {2168-2208}, month = oct }
2024
- SwinTExCo
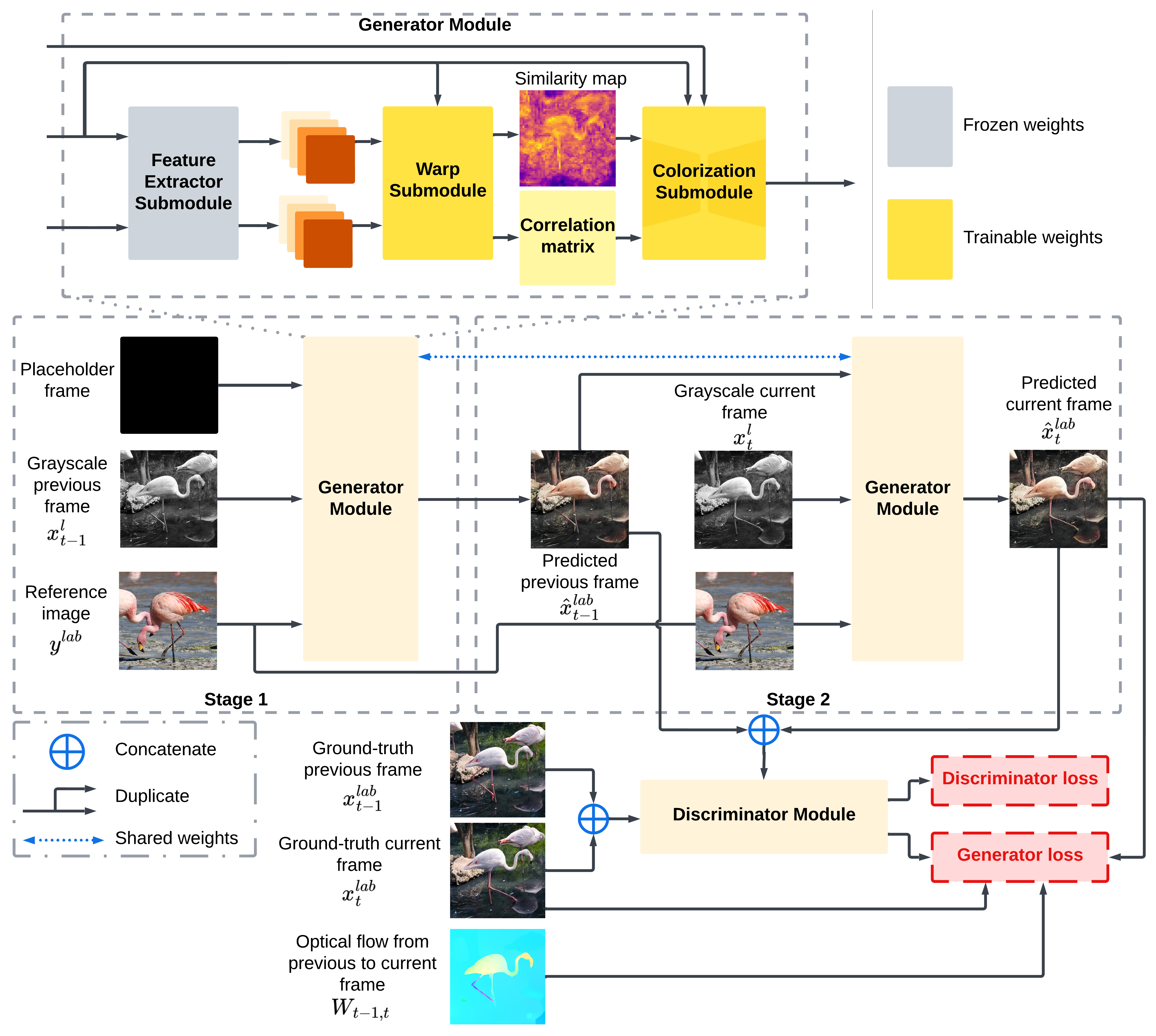 SwinTExCo: Exemplar-based video colorization using Swin TransformerDuong Thanh Tran, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Trung Thanh Pham, and 5 more authorsExpert Systems with Applications, Oct 2024
SwinTExCo: Exemplar-based video colorization using Swin TransformerDuong Thanh Tran, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Trung Thanh Pham, and 5 more authorsExpert Systems with Applications, Oct 2024Video colorization represents a compelling domain within the field of Computer Vision. The traditional approach in this field relies on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to extract features from each video frame and employs a recurrent network to learn information between video frames. While demonstrating considerable success in colorization, most traditional CNNs suffer from a limited receptive field size, capturing local information within a fixed-sized window. Consequently, they struggle to directly grasp long-range dependencies or pixel relationships that span large image or video frame areas. To address this limitation, recent advancements in the field have leveraged Vision Transformer (ViT) and their variants to enhance performance. This article introduces Swin Transformer Exemplar-based Video Colorization (SwinTExCo), an end-to-end model for the video colorization process that incorporates the Swin Transformer architecture as the backbone. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms many other state-of-the-art methods in both quantitative and qualitative metrics. The achievements of this research have significant implications for the domain of documentary and history video restoration, contributing to the broader goal of preserving cultural heritage and facilitating a deeper understanding of historical events through enhanced audiovisual materials.
@article{TRAN2024125437, bibtex_show = true, title = {SwinTExCo: Exemplar-based video colorization using Swin Transformer}, journal = {Expert Systems with Applications}, pages = {125437}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Elsevier}, issn = {0957-4174}, dimensions = {true}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125437}, author = {Tran, Duong Thanh and Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Pham, Trung Thanh and Tran, Phuong-Nam and Vu, Thuy-Duong Thi and Nguyen, Cuong Tuan and Dang-Ngoc, Hanh and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, keywords = {Computer vision, Image colorization, Video colorization, Exemplar-based, Vision transformer, Swin transformer}, } - Mol2Lang-VLM
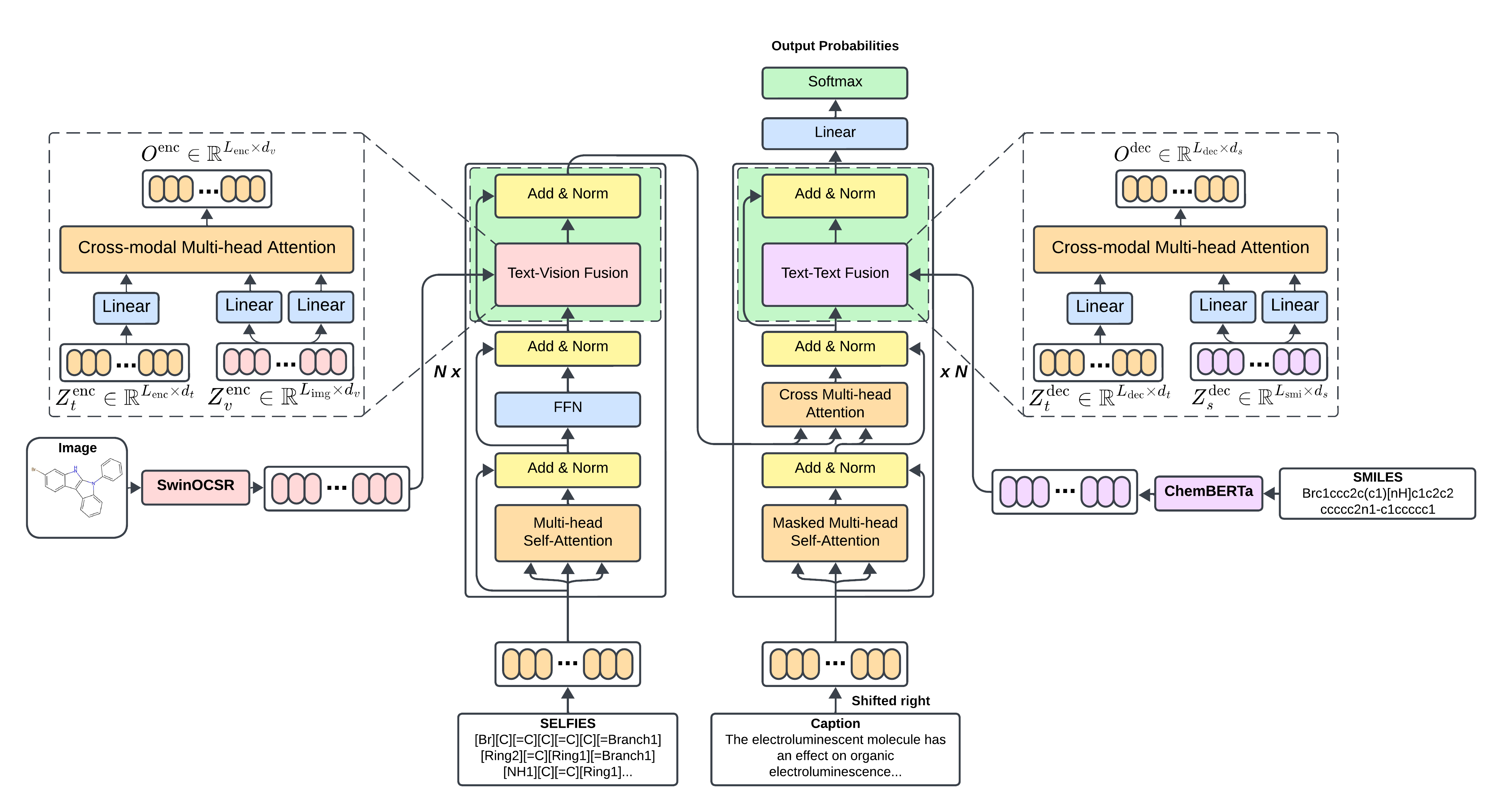 Mol2Lang-VLM: Vision- and Text-Guided Generative Pre-trained Language Models for Advancing Molecule Captioning through Multimodal FusionDuong Thanh Tran(†), Nhat Truong Pham(†), Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Language + Molecules (L+M 2024) , Aug 2024
Mol2Lang-VLM: Vision- and Text-Guided Generative Pre-trained Language Models for Advancing Molecule Captioning through Multimodal FusionDuong Thanh Tran(†), Nhat Truong Pham(†), Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Language + Molecules (L+M 2024) , Aug 2024This paper introduces Mol2Lang-VLM, an enhanced method for refining generative pre-trained language models for molecule captioning using multimodal features to achieve more accurate caption generation. Our approach leverages the encoder and decoder blocks of the Transformer-based architecture by introducing third sub-layers into both. Specifically, we insert sub-layers in the encoder to fuse features from SELFIES strings and molecular images, while the decoder fuses features from SMILES strings and their corresponding descriptions. Moreover, cross multi-head attention is employed instead of common multi-head attention to enable the decoder to attend to the encoder’s output, thereby integrating the encoded contextual information for better and more accurate caption generation. Performance evaluation on the CheBI-20 and L+M-24 benchmark datasets demonstrates Mol2Lang-VLM’s superiority, achieving higher accuracy and quality in caption generation compared to existing methods. Our code and pre-processed data are available at https://github.com/nhattruongpham/mol-lang-bridge/tree/mol2lang/.
@inproceedings{tran-etal-2024-mol2lang, bibtex_show = true, title = {{M}ol2{L}ang-{VLM}: Vision- and Text-Guided Generative Pre-trained Language Models for Advancing Molecule Captioning through Multimodal Fusion}, author = {Tran<sup>(†)</sup>, Duong Thanh and Pham<sup>(†)</sup>, Nhat Truong and Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Manavalan, Balachandran}, editor = {Edwards, Carl and Wang, Qingyun and Li, Manling and Zhao, Lawrence and Hope, Tom and Ji, Heng}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Language + Molecules (L+M 2024)}, month = aug, year = {2024}, address = {Bangkok, Thailand}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, pages = {97--102}, } - Lang2Mol-Diff
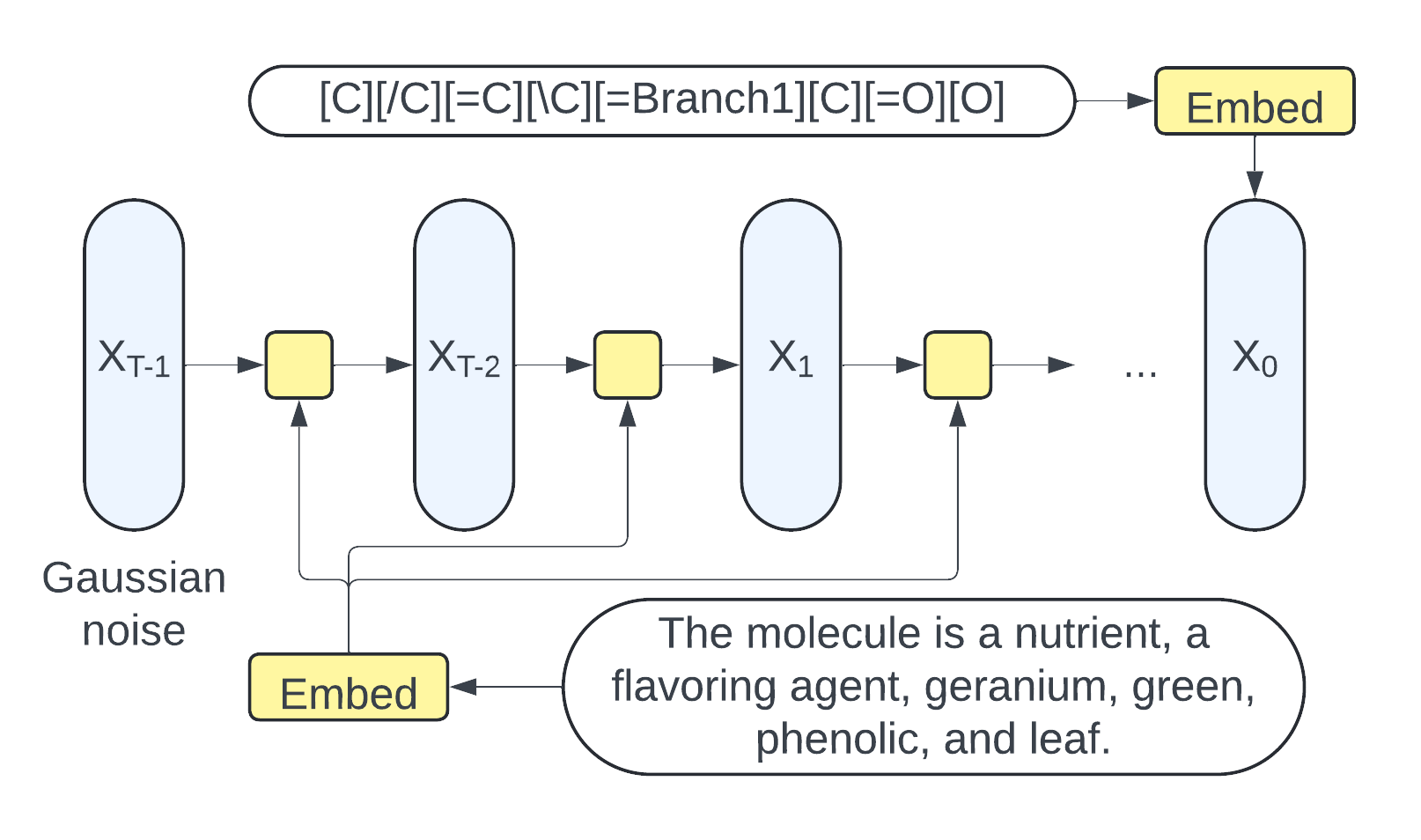 Lang2Mol-Diff: A Diffusion-Based Generative Model for Language-to-Molecule Translation Leveraging SELFIES RepresentationNguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen(†), Nhat Truong Pham(†), Duong Thanh Tran, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Language + Molecules (L+M 2024) , Aug 2024
Lang2Mol-Diff: A Diffusion-Based Generative Model for Language-to-Molecule Translation Leveraging SELFIES RepresentationNguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen(†), Nhat Truong Pham(†), Duong Thanh Tran, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Language + Molecules (L+M 2024) , Aug 2024Generating de novo molecules from textual descriptions is challenging due to potential issues with molecule validity in SMILES representation and limitations of autoregressive models. This work introduces Lang2Mol-Diff, a diffusion-based language-to-molecule generative model using the SELFIES representation. Specifically, Lang2Mol-Diff leverages the strengths of two state-of-the-art molecular generative models: BioT5 and TGM-DLM. By employing BioT5 to tokenize the SELFIES representation, Lang2Mol-Diff addresses the validity issues associated with SMILES strings. Additionally, it incorporates a text diffusion mechanism from TGM-DLM to overcome the limitations of autoregressive models in this domain. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to leverage the diffusion mechanism for text-based de novo molecule generation using the SELFIES molecular string representation. Performance evaluation on the L+M-24 benchmark dataset shows that Lang2Mol-Diff outperforms all existing methods for molecule generation in terms of validity. Our code and pre-processed data are available at https://github.com/nhattruongpham/mol-lang-bridge/tree/lang2mol/.
@inproceedings{nguyen-etal-2024-lang2mol, bibtex_show = true, title = {{L}ang2{M}ol-Diff: A Diffusion-Based Generative Model for Language-to-Molecule Translation Leveraging {SELFIES} Representation}, author = {Nguyen<sup>(†)</sup>, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Pham<sup>(†)</sup>, Nhat Truong and Tran, Duong Thanh and Manavalan, Balachandran}, editor = {Edwards, Carl and Wang, Qingyun and Li, Manling and Zhao, Lawrence and Hope, Tom and Ji, Heng}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Language + Molecules (L+M 2024)}, month = aug, year = {2024}, address = {Bangkok, Thailand}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, pages = {128--134}, }
2023
- Vitexco
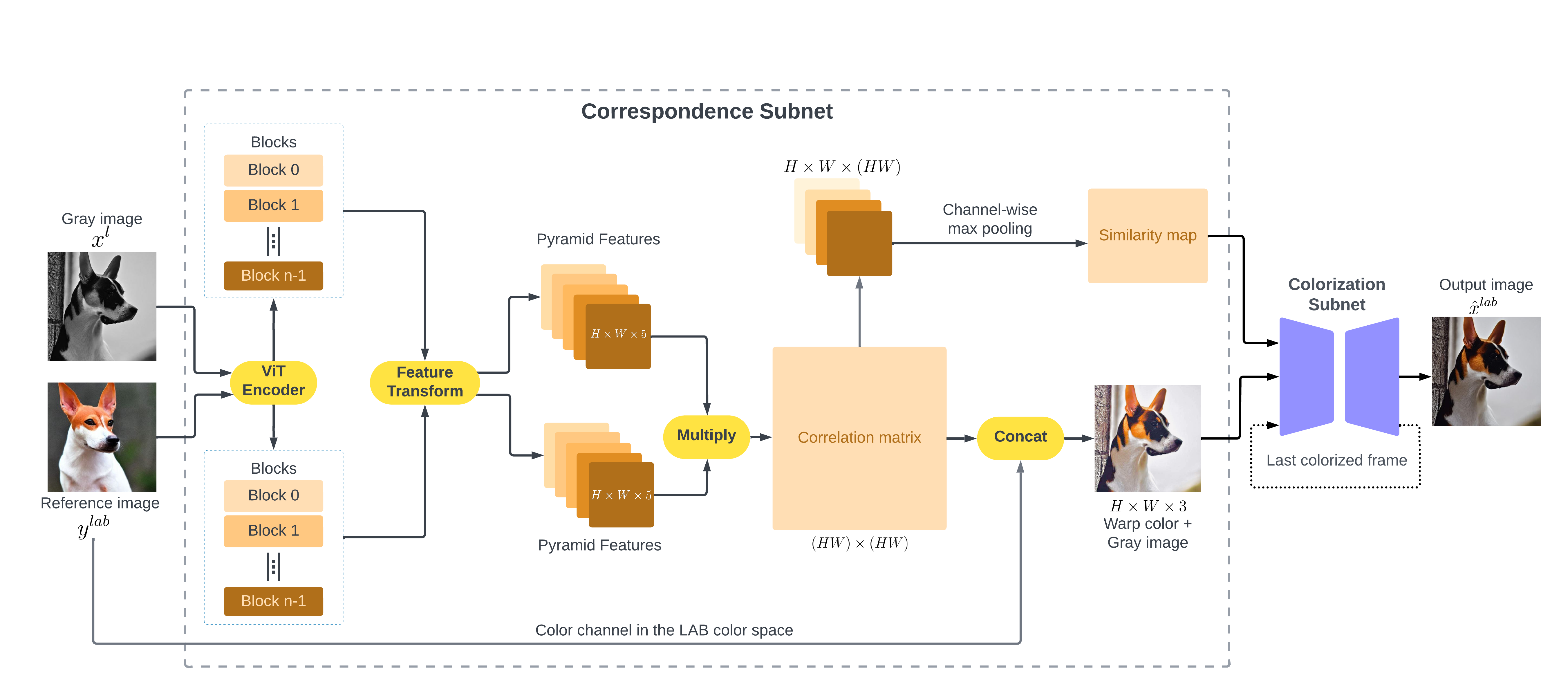 Vitexco: Exemplar-based Video Colorization using Vision TransformerDuong Thanh Tran, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Trung Thanh Pham, and 3 more authorsIn 2023 14th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC) , Aug 2023
Vitexco: Exemplar-based Video Colorization using Vision TransformerDuong Thanh Tran, Nguyen Doan Hieu Nguyen, Trung Thanh Pham, and 3 more authorsIn 2023 14th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC) , Aug 2023In the field of image and video colorization, the existing research employs a CNN to extract information from each video frame. However, due to the local nature of a kernel, it is challenging for CNN to capture the relationships between each pixel and others in an image, leading to inaccurate colorization. To solve this issue, we introduce an end-to-end network called Vitexco for colorizing videos. Vitexco utilizes the power of the Vision Transformer (ViT) to capture the relationships among all pixels in a frame with each other, providing a more effective method for colorizing video frames. We evaluate our approach on DAVIS datasets and demonstrate that it outperforms the state-of-the-art methods regarding color accuracy and visual quality. Our findings suggest that using a ViT can significantly enhance the performance of video colorization.
@inproceedings{10393505, bibtex_show = true, author = {Tran, Duong Thanh and Nguyen, Nguyen Doan Hieu and Pham, Trung Thanh and Tran, Phuong-Nam and Vu, Thuy-Duong Thi and Dang, Duc Ngoc Minh}, title = {<b><i>Vitexco</i></b>: Exemplar-based Video Colorization using Vision Transformer}, booktitle = {2023 14th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC)}, publisher = {{IEEE}}, year = {2023}, pages = {59-64}, keywords = {Measurement;Visualization;Image color analysis;Transformers;Information and communication technology;Data mining;Kernel;image colorization;video colorization;exemplar-based;vision transformer}, doi = {10.1109/ICTC58733.2023.10393505}, dimensions = {true}, }